Ask Learn
Preview
Ask Learn is an AI assistant that can answer questions, clarify concepts, and define terms using trusted Microsoft documentation.
Please sign in to use Ask Learn.
Sign inThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article is part of the series of blogs on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). In this article I am going to share my experience of setting up Elasticsearch, Logstash and Kibana cluster in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and consume messages from Event Hub. After the end of this article, we are going to have fully functional ELK stack with Azure Event Hub integration.
A sample client App (e.g. IOT device) will be publishing messages to Event Hub and these messages will be ingested into Elasticsearch using 'Azure Event Hub' plugin of Logstash. This article needs x-pack features of Elasticsearch thus I will show steps needed to activate trial license.
The second part of this series goes through steps needed to enable Azure AD SAML based single sign on to secure Elasticsearch and Kibana hosted in AKS. The third part of this series goes through steps needed to ingest Azure Redis Cache messages into Elasticsearch using Logstash's Redis plugin.
The dev tools used to develop these components are Visual Studio for Mac/Visual Studio 2017, AKS Dashboard as well as kubectl commands are used to create/manager Kubernetes resources in AKS.
In case you don’t have AKS cluster up and running, please go through this article to Create AKS Cluster. Once AKS cluster is up and running, you can go through the rest of the article. The code snippets in this article are mostly yaml snippets and are included for reference only as formatting may get distorted thus please refer to GitHub repository for formatted resources.
Event hub messages will be ingested into Elasticsearch using Logstash pipeline, thus first resource I am going to create is Event Hub. Please follow steps listed in this article to create an Event Hub. The main pointers are
The next resource which you will need to create is Azure Blob Storage. Please follow steps listed in this article to create a storage account. Once storage account is created, create Blob Service-> Blobs. The main pointers are
AzureEventHubSample project is client app to send messages to Event hub. You will need to update connectionString variable with Event Hub connection string and name of the hub. You can download the source code of this publisher client from Github.
Elasticsearch is a near real time search platform. The steps needed to deploy Elasticsearch to AKS cluster are listed below
Persistent volume claim is needed to store Elasticsearch data. The yaml snippet to create a 5 GB storage is displayed below. The StatefulSet resource is going to mount files to this storage claim. You can read more about Persistent Volumes. apiVersion: v1kind: PersistentVolumeClaimmetadata: name: sample-elasticsearch-data-claimspec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 5Gi
ConfigMaps allow you to decouple configuration aspects from image and a few pointers about the yaml snippet displayed below are
max_local_storage_nodes based on number of Pods apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata: name: sample-elasticsearch-configmap namespace: defaultdata: elasticsearch.yml: | cluster.name: "sample-elasticsearch-cluster" network.host: 0.0.0.0 discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 1 #Update max_local_storage_nodes value based on number of nodes node.max_local_storage_nodes: 1 xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.monitoring.collection.enabled: true role_mapping.yml: |
You can read more about ConfigMap.
The next step is to create a Kubernetes Service for Elasticsearch. As you can see in yaml snippet below, port 9200/9300 is defined and type is ClusterIP i.e. this service doesn't has external endpoints. Kubernetes will use to selector 'service: sample-elasticsearch' to map to the deployment as you are going to see next. You can read more about Services. apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: sample-elasticsearch labels: service: sample-elasticsearchspec: type: ClusterIP selector: service: sample-elasticsearch ports: - name: http port: 9200 targetPort: 9200 protocol: TCP - name: transport port: 9300 targetPort: 9300 protocol: TCP
Kubernetes StatefulSet is the workload API used to manage stateful applications. You can read more about StatefulSets. The yaml snippet to create a StatefulSet is displayed below and a few pointers are
service: sample-elasticsearch matches to the selector defined in the service.replicas: 1 which means that only one instance of Pod will be created by Kubernetes. You can update this value as needed, however you will need to update ConfigMap value .max_local_storage_nodes: 1 too.image:docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:6.4.1.- name: "TAKE_FILE_OWNERSHIP" value: “1”. The alternate option is to grant write access by adding an initcontainer step e.g. command: - sh - -c - chown -R 1000:1000 /usr/share/elasticsearch/data. You can read more at Elasticsearch Docker.vm.max_map_count=262144 by adding an initcontainer step. You can read more about Elasticsearch virtual memory.configMap: name: sample-elasticsearch-configmap.persistentVolumeClaim: claimName:sample-elasticsearch-data-claim.resources:limits:. You can read more about Assign CPU Resources to Containers and Pods apiVersion: apps/v1kind: StatefulSetmetadata: name: sample-elasticsearch labels: service: sample-elasticsearchspec: serviceName: sample-elasticsearch # Number of PODS replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: service: sample-elasticsearch template: metadata: labels: service: sample-elasticsearch spec: terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 15 initContainers: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/vm-max-map-count.html - name: increase-the-vm-max-map-count image: busybox command: - sysctl - -w - vm.max_map_count=262144 securityContext: privileged: true containers: - name: sample-elasticsearch image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:6.4.1 resources: limits: cpu: 2000m memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 100m memory: 1Gi ports: - containerPort: 9200 name: http - containerPort: 9300 name: tcp env: - name: cluster.name value: "sample-elasticsearch-cluster" - name: "xpack.security.enabled" value: "true" - name: "TAKE_FILE_OWNERSHIP" value: “1” volumeMounts: - name: sample-elasticsearch-data-claim mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data - name: sample-elasticsearch-configmap mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml subPath: elasticsearch.yml - name: sample-elasticsearch-configmap mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/config/role_mapping.yml subPath: role_mapping.yml volumes: - name: sample-elasticsearch-data-claim persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: sample-elasticsearch-data-claim - name: sample-elasticsearch-configmap configMap: name: sample-elasticsearch-configmap
By default Elasticsearch will be deployed with basic license. After Elasticsearch is deployed, the next step is to activate trail license of Elasticsearch to use x-pack features of Elasticsearch.
The steps needed to activate trail license are
kubectl port-forward sample-elasticsearch-0 9200:9200 and now you can access Elasticsearch endpoint at https://localhost:9200. POST https://localhost:9200/_xpack/license/start_trial?acknowledge=true request from any rest client. This is going to activate the trial license.https://localhost:9200/_xpack/license request from any rest client.x-pack security feature of Elasticsearch is used to secure access thus we now need to setup passwords for built-in user accounts and the steps are
kubectl exec -ti sample-elasticsearch-0 bashbin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactive to setup built-in user passwords interactively. For this sample I have specified same password i.e. Password1$ for all accounts thus you will need to change password you specified in a few places in source code.Kibana lets you visualize your Elasticsearch data and navigate the Elastic Stack. The steps needed to deploy Kibana to AKS are listed below
The yaml snippet to create this resource is displayed below and a few pointers are
kibana.yml file will be mounted from ConfigMapelasticsearch.url: https://sample-elasticsearch:9200elasticsearch.password: Password1$ based on your specified password for kibana (built-in) user apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata: name: sample-kibana-configmap namespace: defaultdata: kibana.yml: | server.name: sample-kibana server.host: "0" elasticsearch.url: https://sample-elasticsearch:9200 xpack.monitoring.ui.container.elasticsearch.enabled: true elasticsearch.username: kibana elasticsearch.password: Password1$
The next step is to create a Kubernetes Service for Kibana. As you can see in yaml snippet below, port 80 is defined and type is LoadBalancer i.e. this service has external endpoints. Kubernetes will use to selector 'component: sample-kibana' to map to the deployment as you are going to see next. The creation of this service is going to take a while and once done you can get the external endpoint of this service either by opening AKS Dashboard or running Kubectl command kubectl describe services sample-kibana.
apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata: name: sample-kibana labels: component: sample-kibanaspec: type: LoadBalancer selector: component: sample-kibana ports: - name: http port: 80 targetPort: http
The next step is to create a Kubernetes Deployment for Kibana. The yaml snippet is displayed below and a few pointers are
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:6.4.1replicas: 1component: sample-kibana has to match the selector defined in the serviceconfigMap: name: sample-kibana-configmap apiVersion: apps/v1beta1kind: Deploymentmetadata: name: sample-kibana labels: component: sample-kibanaspec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: component: sample-kibana template: metadata: labels: component: sample-kibana spec: containers: - name: sample-kibana image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:6.4.1 resources: limits: cpu: 1000m requests: cpu: 100m ports: - containerPort: 5601 name: http volumeMounts: - name: sample-kibana-configmap mountPath: /usr/share/kibana/config/kibana.yml subPath: kibana.yml resources: {} terminationMessagePath: "/dev/termination-log" terminationMessagePolicy: File imagePullPolicy: Always securityContext: privileged: false volumes: - name: sample-kibana-configmap configMap: name: sample-kibana-configmap restartPolicy: Always terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 5 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst securityContext: {} schedulerName: default-scheduler
Open the external endpoint of Kibana service once deployment is completed. Since x-pack security is enabled, Kibana will prompt for credentials.
Logstash is data processing pipeline that ingests data from a multitude of sources simultaneously, transforms it, and then sends it to Elasticsearch. Logstash will use Azure Event Hub plugin to ingest data into Elasticsearch. The steps needed to deploy Logstash to AKS are listed below
The yaml snippet to create ConfigMap is displayed below and a few pointers are
logstash.yml file will be mounted from ConfigMappipelines.yml file will be mounted from ConfigMap. Multiple pipelines can be defined in this file e.g. you can see that AzureEventHubs pipeline is defined.azureeventhub.cfg file will be mounted from ConfigMap. The Logstash event processing pipeline has three stages: inputs → filters → outputs. This file defines the logstash pipeline for Azure Event Hub.
{AZURE_EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING} and {STORAGE_ACCOUNT_CONNECTION_STRING} values based on your Event Hub and Storage Account values.EntityPath in case your event hub is named differently then logstash.storage_container in case your storage container is named differently than logstash.consumer_group in case your consumer group is different than $Default. Specifying $Default isn't an ideal option.index => "azureeventhub-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}logstash.conf file will be mounted from ConfigMapxpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.url: https://sample-elasticsearch:9200xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: Password1$ based on your specified password for logstash_system (built-in) user.hosts => [ "sample-elasticsearch:9200" ]password => "Password1$" to the specified password of your elastic (built-in) user apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata: name: sample-logstash-configmap namespace: defaultdata: logstash.yml: | xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.url: https://sample-elasticsearch:9200 dead_letter_queue.enable: true xpack.monitoring.enabled: true xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: logstash_system xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: Password1$ pipelines.yml: | - pipeline.id: azureeventhubs path.config: "/usr/share/logstash/azureeventhubs.cfg" azureeventhubs.cfg: | input { azure_event_hubs { event_hub_connections => ["{AZURE_EVENT_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING};EntityPath=logstash"] threads => 2 decorate_events => true consumer_group => "$Default" storage_connection => "{STORAGE_ACCOUNT_CONNECTION_STRING}" storage_container => "logstash" } } filter { } output { elasticsearch { hosts => [ "sample-elasticsearch:9200" ] user => "elastic" password => "Password1$" index => "azureeventhub-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } logstash.conf: |
The next step is to create a Kubernetes Service for Logstash. As you can see in yaml snippet below, port 80 is defined and type is ClusterIP i.e. this service has no external endpoints. Kubernetes will use to selector 'component: sample-logstash' to map to the deployment as you are going to see next.
apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata: name: sample-logstash labels: component: sample-logstashspec: type: ClusterIP selector: component: sample-logstash ports: - name: http port: 80 targetPort: http
The next step is to create a Kubernetes Deployment for Logstash. The yaml snippet is displayed below and a few pointers are
docker.elastic.co/logstash/logstash:6.4.1replicas: 1component: sample-logstash has to match the selector defined in the serviceconfigMap: name: sample-logstash-configmap apiVersion: apps/v1beta1kind: Deploymentmetadata: name: sample-logstash labels: component: sample-logstashspec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: component: sample-logstash template: metadata: labels: component: sample-logstash spec: containers: - name: sample-logstash image: docker.elastic.co/logstash/logstash:6.4.1 volumeMounts: - name: sample-logstash-configmap mountPath: /usr/share/logstash/config/logstash.yml subPath: logstash.yml - name: sample-logstash-configmap mountPath: /usr/share/logstash/pipeline/logstash.conf subPath: logstash.conf - name: sample-logstash-configmap mountPath: /usr/share/logstash/azureeventhubs.cfg subPath: azureeventhubs.cfg - name: sample-logstash-configmap mountPath: /usr/share/logstash/config/pipelines.yml subPath: pipelines.yml resources: limits: cpu: 1000m requests: cpu: 100m ports: - containerPort: 5601 name: http volumes: - name: sample-logstash-configmap configMap: name: sample-logstash-configmap
As mentioned earlier, Logstash will use azure_event_hubs plugin to ingest data into Elasticsearch. You can get installed plugins list by following steps listed below
kubectl exec -ti {Logstash_Pod_Name} bash to connect to Logstash POD.bin/logstash-plugin list to see installed pluginsAfter all resources are deployed to AKS, run client app to send messages to Event hub. Open Kibana and you will see ELK stack statistics in Monitoring section. The number of messages sent by client App to Event hub will be displayed in Logstash's Events received and events emitted statistics.
The Discover tab of Kibana will display events ingested into Elasticsearch once you create index filters e.g. I have selected index filter as 'azureeventhub*' and you can see that this index naming convention was defined in azureeventshub.cfg pipelineindex => "azureeventhub-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}.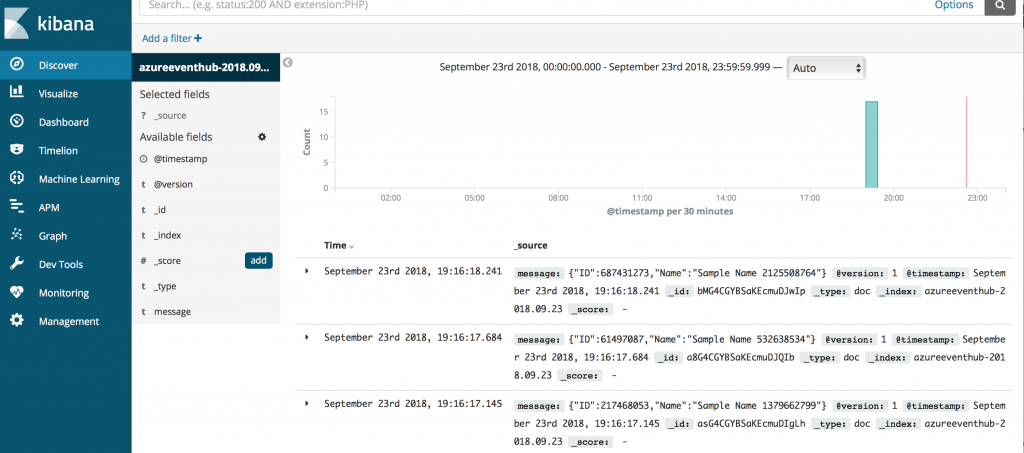
You can download source code for this article from GitHub repository
The second part of this series is Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Azure AD SAML based Single Sign on to secure Elasticsearch and Kibana and securing communications in ELK
Ask Learn is an AI assistant that can answer questions, clarify concepts, and define terms using trusted Microsoft documentation.
Please sign in to use Ask Learn.
Sign in