EXEC vs. sp_executeSQL
When we want to execute a TSQL string we can use both EXEC and sp_executesql statements. But there are some very important differences between them
- sp_executesql allows for statements to be parameterized
- Therefore It’s more secure than EXEC in terms of SQL injection
- sp_executesql can leverage cached query plans.
- The TSQL string is built only one time, after that every time same query is called with sp_executesql, SQL Server retrieves the query plan from cache and reuses it
- Temp tables created in EXEC can not use temp table caching mechanism
Let’s make a demo to see above number 2 behavior
Use AdventureWorks2012
GO
--DO NOT RUN this script on Production environment
--Clear the plan cache
dbcc freeproccache
--Use EXEC to execute a TSQL string
declare @str varchar(max)='',
@param1 varchar(50)='',
@param2 varchar(50)=''
set @param1='1'
set @param2='2'
set @str='select * from Person.Address where AddressID in ('+@param1+','+@param2+')'
exec(@str)
--Execute the same query with different paramaters
declare @str varchar(max)='',
@param1 varchar(50)='',
@param2 varchar(50)=''
set @param1='3'
set @param2='4'
set @str='select * from Person.Address where AddressID in ('+@param1+','+@param2+')'
exec(@str)
--Look at the cached query plans
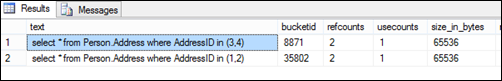
select st.text,*
from sys.dm_exec_cached_plans cp
cross apply sys.dm_exec_sql_text(cp.plan_handle) st
where (st.text like '%select * from Person.Address%')
and st.text not like '%select st.text%'
As you see 2 different query plans(1 for each query) are cached. Because EXEC does not allow for statements to be parameterized. They are similar to ad-hoc queries.
Let's do same example with sp_executesql
--Let's do same example with sp_executesql
Use AdventureWorks2012
GO
--DO NOT RUN this script on Production environment
--Clear the plan cache
dbcc freeproccache
--sp_executesql 1
declare @param1 int,
@param2 int
set @param1=1
set @param2=2
exec sp_executesql N'select * from Person.Address where AddressID in (@1,@2)'
,N'@1 int, @2 int'
,@param1, @param2
--sp_executesql 2
declare @param1 int,
@param2 int
set @param1=3
set @param2=4
exec sp_executesql N'select * from Person.Address where AddressID in (@1,@2)'
,N'@1 int, @2 int'
,@param1, @param2
--Look at the cached query plans
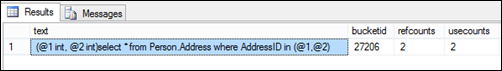
select st.text,*
from sys.dm_exec_cached_plans cp
cross apply sys.dm_exec_sql_text(cp.plan_handle) st
where (st.text like '%select * from Person.Address%')
and st.text not like '%select st.text%'
2 different parameter sets used same query plan because as you can see cached query plan is parameterized.