10 Reasons to Upgrade SAP systems to Windows 2008 / Windows 2008 R2
Benefits of upgrading Windows 2003 to Windows 2008 for SAP Systems
Microsoft has released Windows 2008 (Windows 6.0) several years ago and this release has proved very popular among SAP customers. Today all new SAP implementations that we are involved in are deployed on Windows 2008. SAP fully supports Windows 2008 for all ABAP and Java components of Netweaver Basis 7.0 and later. Details of the support status of all SAP components can be found in the SAP PAM.
Microsoft has recently released Windows 2008 R2 (Windows 6.1) which includes several key enhancements for SAP customers. Windows 2008 R2 includes memory and IO performance enhancements, support for 256 CPU cores, more sophisticated power saving features and the ability to greatly reduce security updates and patching by completely removing Internet Explorer (KB957700).
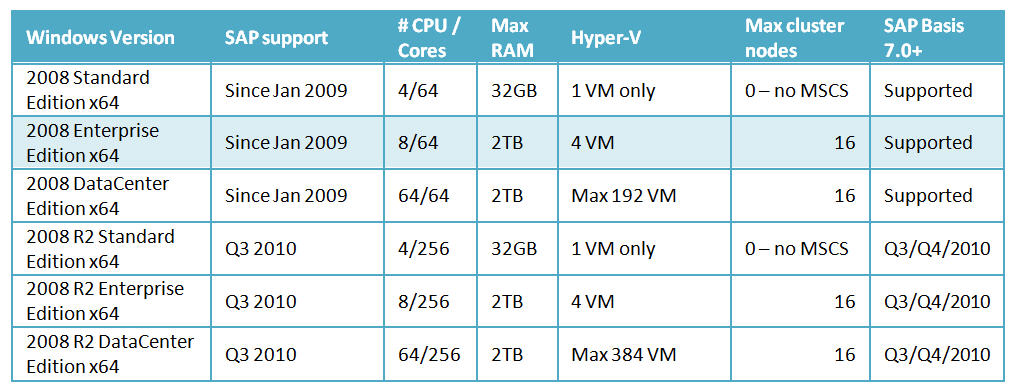
Since the Windows 2008 R2 Operating System kernel changed substantially to enable support of 256 CPUs, compared to Windows 2008 (winver 6.0), SAP are still in the process of validating Windows 2008 R2. Support for Windows 2008 R2 is expected around September or October 2010. Already some products such as SAP Content Server 6.40 are fully supported on Windows 2008 R2. This blog will have a post when Windows 2008 R2 is going to be supported and the PAM will be updated as well as OSS Note 1383873
10 Reasons Why to Upgrade from Windows 2003 to Windows 2008
Customers running on Windows 2003 today can quickly and easily upgrade to Windows 2008 and soon Windows 2008 R2. Microsoft recommends that larger customers plan to move to Windows 2008/R2 soon. Larger customers have seen great improvements in the performance and reliability of their SAP systems after upgrading to Windows 2008.
1. Consolidation with Windows Hyper-V
Windows Hyper-V is delivered free of charge with Windows 2008 and is very popular amongst SAP customers to reduce server sprawl and improve utilization. The Microsoft Whitepaper on Hyper-V for SAP systems can be found here.
Windows Hyper-V R2 dramatically lowers the overhead of virtualization by supporting AMD and Intel Second Level Address Translation.
Live Migration offers similar functionality to VMWare VMotion at much lower cost.
Boot from VHD and hot add/remove SCSI disks are also supported in Hyper-V R2. Windows 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 plans to add Dynamic memory.
The support, configuration and deployment of Hyper-V is contained in OSS Note 1409608 - Virtualization on Windows and Note 1246467 - Windows Hyper-V Configuration Guideline.
2. Security & Patching
Windows 2008 R2 installs with a very bare minimum installation footprint. Starting from Windows 2008 Microsoft deploys minimum functionality with the default Windows Server installation. Customers can install additional Features & Roles. It is recommended that customers do not deploy any additional Role or Features for SAP systems such as "Desktop Experience". The SAP installer will add "File Sharing" automatically. This is required to share the SAPLOC and SAPMNT.
Around 80-90% of Windows Security patches are for or depend on Internet Explorer. Windows 2008 R2 allows the complete removal of Internet Explorer KB957700.
Windows 2008 R2 has improved Firewall and combined with a smaller installation footprint there is a greatly reduced attach surface area. The removal of Internet Explorer lowers the patching requirements to a similar level as UNIX operating systems.
Many customers report that after upgrading to Windows 2008 they review each security patch contents via the Microsoft Security bulletin website and only deploy the patches that apply to their configuration on their SAP systems (example: not deploying IE patches if IE is removed, not deploying patches that are for Domain controllers etc)
3. Performance
When Windows 2003 was engineered in 2002 and 2003 a typical server had either 2 or 4 CPU and 2GB to 4GB of RAM. Intel processors were all 32bit and technologies like multi-core and hyper-threading did not exist. Today a typical 4CPU Nehalem EX server has 32 cores and hyper-threading presents 64 logical CPU cores to the Windows operating system - these systems are very powerful and sized with > 55,000 SAPS. Some SAP on SQL Server customers use 512GB of memory on their database servers. Windows 2003 has shown good scalability until recent years when hardware platforms have evolved very quickly. Windows 2008 and Windows 2008 R2 show much better performance especially for large scale customers.
4. Improvements in Clustering
Windows 2008 introduces completely new clustering technology. Clustering in Windows 2008 has been redeveloped and new quorum models introduced. The Cluster Validation Wizard, new administration tool and Quorum models are of great benefit for SAP customers. SAP customers are suggested to evaluate using the "Node and File Share Majority" quorum model as detailed in this document from HP.
5. Improved Memory Handling
Windows 2008 resolves several memory issues in Windows 2003 on larger systems. These are described in KB918483, KB920739, KB938486 and KB931308. In addition the problem described in KB976618 has much less impact on Windows 2008 than it does on Windows 2003. These issues are discussed in OSS Note 1009297 - Windows Server 2003 Family High Paging Rates and Note OSS 1316558
Windows 2008 R2 further enhances memory handling with great improvements and the total elimination of the memory issue described in KB976618 and OSS Note 1416152 - High paging rates for backup in Windows server 2003 and 2008
Only 64 bit editions of Windows 2008 or higher are supported. It is no longer permitted to use 32 bit versions of Windows for SAP systems. Microsoft and SAP recommend moving off 32 bit version of Windows immediately. Note 1280759 - SAP recommends only 64-Bit Windows for SAP Appl. Servers. Windows 2008 & higher also eliminates the issues in OSS Note 1316558, 1357247 and 1320013. These issues mostly relate to CRM systems. In addition Flat Memory can be used on Windows 2008 or higher as per OSS Note 1002587
6. Improved memory copy & IO handling
Windows 2008 R2 further enhances memory & IO handling with great improvements to the Page Frame Number lock database & dispatcher lock. In memory copies and massively parallel IO benefit from the removal of Global locks on the PFN database.
Windows 2008 resolves the disk track alignment issue described in OSS Note 886337 - IO performance problems due to misaligned disk sectors. Additional enhancements for customers using SAN Storage such as improvements in MPIO are of great benefit. An example is new STORPORT.SYS monitoring
7. Enhanced Reliability Features
Windows Hardware Error Architecture (WHEA) has been enhanced to support Machine Check Architecture (MCA) error recovery, offering the ability to contain and recover from several types of multi-bit ECC errors in memory and cache without operating system or application interruption. Windows Server 2008 R2 includes support for fault tolerate memory synchronization. Fault-tolerant servers contain redundant hardware - from fans and power supplies, to processors and RAM, which run in lockstep with each other. Nehalem EX Enterprise Features are supported in Windows 2008 R2
8. Network Stack Enhancements
Windows 2008 adds support for TCPIP offload engines and resolves the problem described in KB942861 and OSS Note 392892 - DBIF_RSQL_SQL_ERROR (SQL error 0 or 11). Jumbo Frames are supported for Hyper-V iSCSI disks greatly improving performance
9. Improved Manageability & Power Consumption
PowerShell 2.0, Best Practices Analyzer and Power Management are all added in Windows 2008 R2. The Core Parking feature allows Windows Server 2008 R2 to consolidate processing onto the fewest number of possible processor cores, and suspends inactive processor cores.
10. End of Mainstream Support for Windows 2003
Windows 2003 is now 7+ years old and is no longer in mainstream support as of 13th July 2010. Further information is in 1177282 Windows: End of Support for SAP Releases. Hardware vendors already stopped supporting Windows 2003 on their new server models and hardware device driver support Windows 2003 will not be available in the future.
How to upgrade from Windows 2003 to Windows 2008 / R2
Currently only SAP Kernel 7.0 systems such as ECC 6.0 are supported on Windows 2008. Releases such as 4.6C and Kernel 6.40 systems are not supported yet.
It is recommended to use the standard SAP System Copy procedures to upgrade from Windows 2003 to Windows 2008 rather than "in place" upgrades. In place upgrades of clustered systems are not supported due to the dramatic improvements in Windows 2008 clustering (which make Windows 2008 incompatible with Windows 2003).
When updating hardware is an ideal time to upgrade the operating system. SAP systems on SQL Server can be quickly and easily copied by follow OSS Note 151603
Useful links
https://h20195.www2.hp.com/V2/getdocument.aspx?docname=4AA2-2644ENW.pdf
https://blogs.msdn.com/b/saptech/archive/2010/04/29/new-best-practices-for-sap-on-hyper-v-white-paper-available.aspx
https://blogs.msdn.com/b/tvoellm/archive/2009/08/05/what-s-new-in-windows-server-2008-r2-hyper-v-performance-and-scale.aspx