Installing SQL Server 2008 R2 Express
The final release of SQL Server 2008 R2 was made publically available on April 21, 2010! SQL Server Express continues to ship in 4 different packages. In this release of Express, we simplified the installation wizard. For the November CTP release, I documented the Express installation process at https://blogs.msdn.com/petersad/archive/2009/11/13/how-to-install-sql-server-2008-r2-express-edition-november-ctp.aspx. The installation process has not changed since the November CTP, except some messages have been changed to indicate the final release.
Here are the Express editions available for download:
Express Package
If your system is? If your system is? If your system is? Microsoft® SQL Server® 2008 R2 Express
Microsoft® SQL Server® 2008 R2 Express with Tools
.
Microsoft® SQL Server® 2008 R2 Express with Advanced Services
.
Microsoft® SQL Server® 2008 R2 Management Studio Express .
The database size limit increased to 10 GB in SQL Server 2008 R2 as mentioned by Krzysztof.
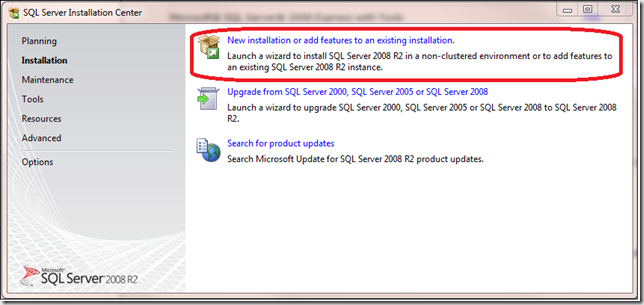
Performing a New Installation:
If you will be performing a new installation, when the Installation Center Launches, choose the following option:
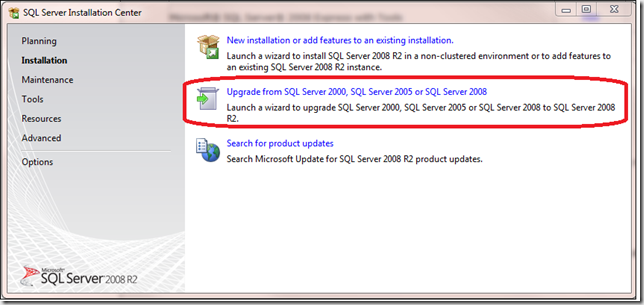
Upgrading
If you would like to upgrade from a earlier version (SQL Server 2005 or SQL Server 2008), when the Installation Center Launches choose the following option:
Embedding
If you develop software applications that embed SQL Server 2008 Express, custom installations are typically required. For more information, see Embedding SQL Server 2008 Express in an Application. We originally create this whitepaper for SQL Server 2008, but everything in the document still applies.
Further Setup Customization
Some SQL Server configuration settings can only be set during install. Once the installation is complete, you cannot change these settings. Any change to the configuration settings would require a new installation of the product. Some settings directly impact how data is stored and organized so changing the configuration setting would require significant data manipulation work in order to preserve the data.
Setting the non-Default Collation
Collations effect how characters (data) for a language or alphabet are recognized and sorted. A majority of SQL Server installations use the default collation. There are some situations where the use of a collation other than the default collation setting would be required.
- Select a BINARY2 collation if binary code point based ordering is acceptable.
- Select a Windows® collation for consistent comparison across data types.
- Use new 100 level collation for better linguistic sorting support. For more information, see Collation and Unicode Support.
- If you plan to migrate a database to the upgraded instance of ssNoVersion, select the collation that matches your existing collation of the database.
For more information, see Collation Settings in Setup.
Enabling Filestream
The Filestream configuration setting specifies where to store unstructured data such as text documents, images or videos. You can store this unstructured data inside the database or outside the database in the NTFS files system. The default setting is to store the data inside the database. Storing outside the database can cause data management complexities. You should consider enabling FILESTREAM if:
- Objects being stored are, on average, larger than 1 MB.
- Fast read access is important.
- You are developing applications that use a middle tier for application logic.
For smaller objects, storing unstructured data in the database often provides better streaming performance.
For more information, see FILESTREAM Overview and FILESTREAM Storage in SQL Server 2008.
Enabling Error Reporting
Enabling the Error Reporting setting allows you to report Windows and SQL Server errors to Microsoft via the internet. Microsoft uses these error reports to improve future releases of SQL Server. Error reports contain only technical data. All error reports are confidential and anonymous.
Customizing Installation Directories
Installation directories are unique folder locations used for placement of:
- Program software
- System database
- User databases and logs
- Temp DB and log
- Backups
During installation, you have the option to changing the default directories for some or all of the folders. Business requirements or environmental factors may dictate specifying directories other than the default.