Shared Assembly Info in Visual Studio Projects
Yesterday I introduced the concept of linked files in Visual Studio solutions with a follow-up on my recommendation for configuring a custom dictionary to eliminate CA1704 code analysis warnings.
Another practical application of linked files is what I refer to as "shared assembly info" -- referring to the assembly attributes that should be the same across all projects in the solution, such as AssemblyCompanyAttribute.
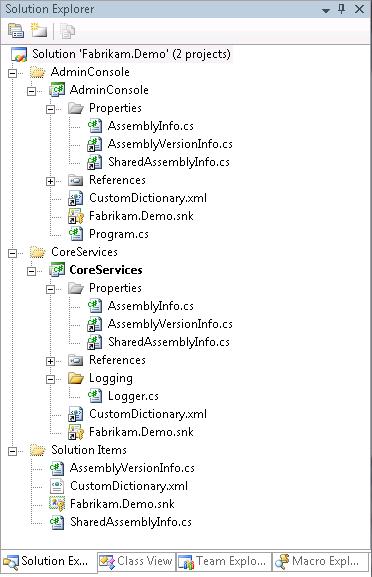
To implement this, create a file in the solution folder named SharedAssemblyInfo.cs and then add a link in each project to SharedAssemblyInfo.cs. You can also move the linked SharedAssemblyInfo.cs into the Properties folder so that it sits side-by-side with the AssemblyInfo.cs that is specific to each project in the solution, as shown below.
Figure 1: Linked SharedAssemblyInfo.cs files in a Visual Studio solution
I recommend placing the following assembly attributes in SharedAssemblyInfo.cs (and, of course, removing them as necessary from the project-specific AssemblyInfo.cs files):
- AssemblyCompany
- AssemblyProduct
- AssemblyCopyright
- AssemblyTrademark
- AssemblyConfiguration
- AssemblyDescription
- CLSCompliant
- ComVisible
- AssemblyVersion
- AssemblyInformationalVersion
The AssemblyInfo.cs files typically have the following assembly attributes:
- AssemblyTitle
- AssemblyCulture
- Guid
Here is a sample SharedAssemblyInfo.cs file:
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
// General Information about an assembly is controlled through the following
// set of attributes. Change these attribute values to modify the information
// associated with an assembly.
[assembly: AssemblyCompany("Fabrikam Technologies")]
[assembly: AssemblyProduct("Demo")]
[assembly: AssemblyCopyright("Copyright ? Fabrikam Technologies 2009")]
[assembly: AssemblyTrademark("")]
// Make it easy to distinguish Debug and Release (i.e. Retail) builds;
// for example, through the file properties window.
#if DEBUG
[assembly: AssemblyConfiguration("Debug")]
[assembly: AssemblyDescription("Flavor=Debug")] // a.k.a. "Comments"
#else
[assembly: AssemblyConfiguration("Retail")]
[assembly: AssemblyDescription("Flavor=Retail")] // a.k.a. "Comments"
#endif
[assembly: CLSCompliant(true)]
// Setting ComVisible to false makes the types in this assembly not visible
// to COM components. If you need to access a type in this assembly from
// COM, set the ComVisible attribute to true on that type.
[assembly: ComVisible(false)]
// Note that the assembly version does not get incremented for every build
// to avoid problems with assembly binding (or requiring a policy or
// <bindingRedirect> in the config file).
//
// The AssemblyFileVersionAttribute is incremented with every build in order
// to distinguish one build from another. AssemblyFileVersion is specified
// in AssemblyVersionInfo.cs so that it can be easily incremented by the
// automated build process.
[assembly: AssemblyVersion("1.0.0.0")]
// By default, the "Product version" shown in the file properties window is
// the same as the value specified for AssemblyFileVersionAttribute.
// Set AssemblyInformationalVersionAttribute to be the same as
// AssemblyVersionAttribute so that the "Product version" in the file
// properties window matches the version displayed in the GAC shell extension.
[assembly: AssemblyInformationalVersion("1.0.0.0")] // a.k.a. "Product version"
Note how the AssemblyConfigurationAttribute and AssemblyDescriptionAttribute are set based on conditional compilation constants (in order to easily distinguish Debug and Release builds).
Here is a sample AssemblyInfo.cs file:
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
// Note: Shared assembly information is specified in SharedAssemblyInfo.cs
// General Information about an assembly is controlled through the following
// set of attributes. Change these attribute values to modify the information
// associated with an assembly.
[assembly: AssemblyTitle("Fabrikam.Demo.CoreServices")]
[assembly: AssemblyCulture("")]
// The following GUID is for the ID of the typelib if this project is exposed to COM
[assembly: Guid("88d50bdd-34bc-414a-98d6-6fefe701d41b")]
In my next post, I'll discuss assembly versioning in more detail.