SQL Performance troubleshooting guide: A walk through
Hi all,
,
This article gives a high level view of isolating SQL Performance issues and logical approach to troubleshoot them.
SQL Server performance issues can be broadly categorized as:
- Overall Server slowness
- Specific query slowness
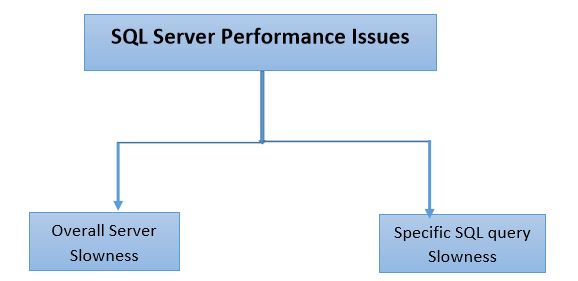
If SQL Server overall performance is slow, then we can categorize the issues as below: If SQL Server overall performance is slow, then we can categorize the issues as below:
- CPU/High Memory bottleneck
- IO Bottleneck
- Blocking
- Network bottleneck
- Latch Waits
- SQL Configuration issues
- Capacity limitation
- SQL/Windows known issues
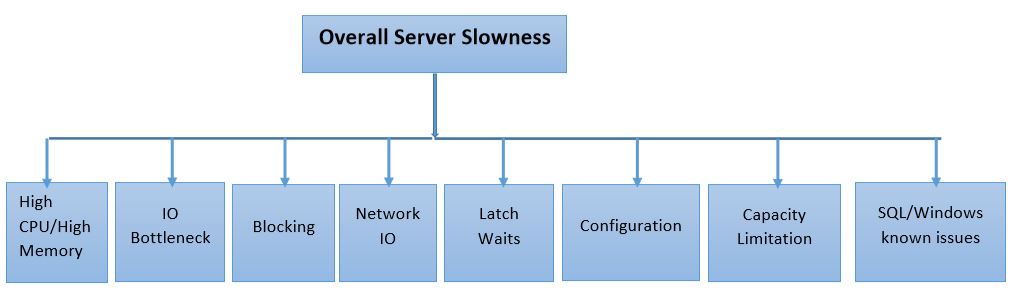
If a specific query is slow, then then the threads executing the query is either in one of the following states:
- Executing/Running
- Waiting
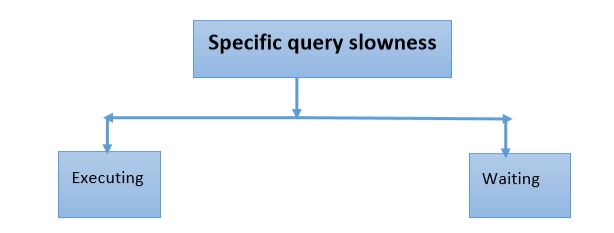
If the query is in executing state and the query execution is slow, the issues can be because of:
- Stale statistics
- High Index/Heap fragmentation
- Bad SQL Execution Plan
- Optimizer timeout
- Long compilations
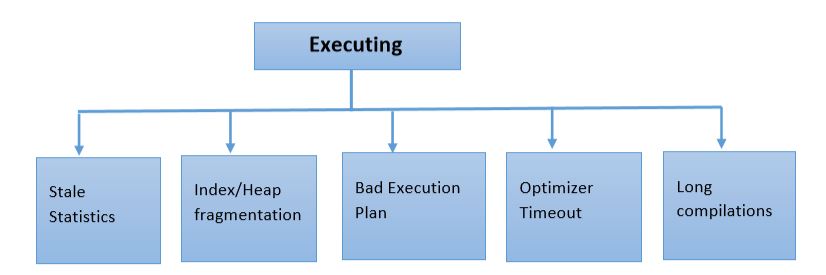
If the query is in waiting state and the query execution is slow, the issues can be because of:
- IO Bottleneck (PAGE IO Latch/Writelog)
- Blocking
- Network IO/Client Fetch
- Latch Waits
- Resource Semaphore waits
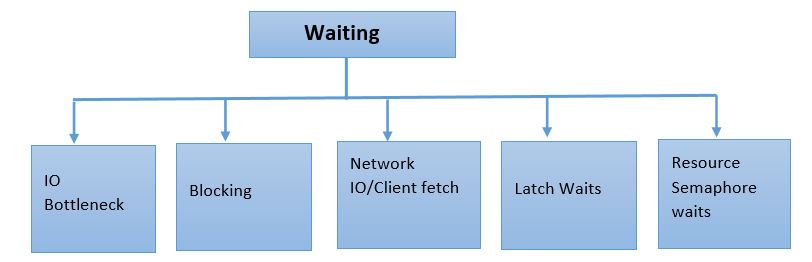
The above walk through is at very high level and refer it as a guide map while troubleshooting performance issues. Based on the bottleneck observed, issue can be drilled further by using dmv's or other troubleshooting tools.
Please share your feedback, questions and/or suggestions.
Thanks,
Don Castelino | Premier Field Engineer | Microsoft
Disclaimer: All posts are provided AS IS with no warranties and confer no rights. Additionally, views expressed here are my own and not those of my employer, Microsoft.