Cloud computing guide for researchers – eBird big data analysis using Microsoft Azure
Citizen scientists all over the world have been helping the Cornell Lab of Ornithology to collect bird observations for 15 years using eBird. This real-time, online checklist program enables birders to record birds they see, keep track of lists, explore maps and graphs, share with the eBird community and contribute to ornithological science and bird conservation.
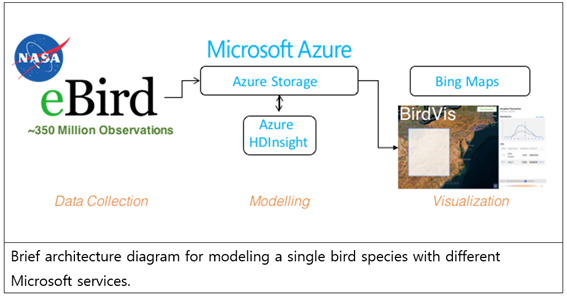
For the researchers, creating high-resolution models using this data is very computationally-intensive. Even a single species model would take around three weeks to run on the mid-sized supercomputer systems available to the team. The researchers needed a more scalable computing platform to be able to generate results for the 700 bird species in North America, to be able to release to conservation staff. The team turned to the Microsoft Azure for Research program that provided them with the cloud computing resources they needed to move their existing R and Linux workloads to the cloud.
They have built a truly scalable, future-proofed system, taking advantage of Microsoft Azure Storage, Microsoft Azure HDInsight Service, Microsoft R Server, Linux Ubuntu, and Apache Hadoop MapReduce and Spark.
The team can now run models that used to take three weeks in just three hours. They no longer have to wait in a queue on their high performance computing cluster, but can use Microsoft Azure on-demand, any time of day or night. It is transforming how they do their research, and now enables them make their research results available to bird conservationists to help protect and improve bird populations.
You can read the full story with technical details by Rashim Gupta here.