OSF 5: Different types of Office Business Applications
[OBA Solution Framework Index]
[UPDATE: For more info on the "OBA RAP for Price Management" (OBA type #5 below) announced yesterday, read the blog posting by Moin here.]
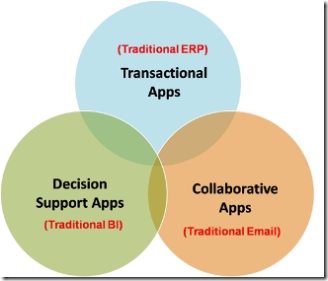
Traditional business applications have mostly either provided collaboration (focus: information sharing), decision support (focus: BI, reporting, planning, event management), or transactional support (e.g. data entry).
However the rich capabilities of the Office system enable applications that can combine elements of collaboration, decision support, and collaboration into a single, unified user experience.
For example, the following screenshots show examples of different types of OBAs, and illustrate how collaboration, decision support and support for business transactions / process are brought together.
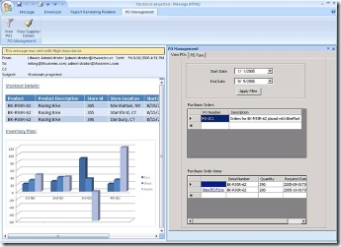
EXAMPLE: An inventory analyst gets an email (COLLABORATION) with information on a stockout. The email shows him tabular / graphical data in Outlook. He can click on the custom ribbon for Procurement, to pull up a list of Purchase Orders in a custom task pane filtered by the item / location / date of the stockout (DECISION SUPPORT). He can then select an order to expedite, which opens up a form within Outlook for him to make changes to the order (BUSINESS TRANSACTION).
This is one type of OBA, where the Office client is connecting to back end systems for data. A list of different types of OBA is as follows:
- Task-centric application built into a stand alone Office client with custom task panes, custom ribbons, and application-level add-ins. For example, a data visualization / analysis application built into Excel.
- Customized office client connecting to back end systems to retrieve data (e.g. inventory analyst application in Outlook above, or Duet v.1.0)
- Application built into the SharePoint portal (Windows SharePoint Services or Microsoft Office SharePoint Server), with all data stored in SharePoint lists, or as documents stored in document libraries. I met a customer (large manufacturing company) that had such an OBA to manage their protfolio of R&D projects - with a SharePoint site set up for each product that was being worked on.
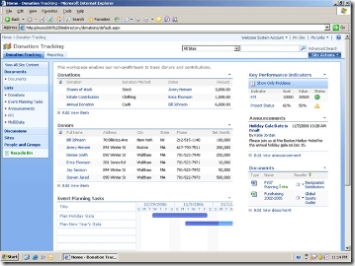
- Application built into the SharePoint portal (Windows SharePoint Services or Microsoft Office SharePoint Server), with connections to back end data stores. The user experience for such an app might look like this:
- End-to-end business solution that is spread across Offfice client apps and SharePoint server. Such a solution would have all the five tiers I listed in my posting here - presentation, collaboration, business process, services, and data. Some examples of these kinds of OBAs are in the OBA Reference Application Packs (RAPs):
- Hosted OBAs used as the delivery mechanism for SaaS (Software as a Service). You can think of Office Live as a great example of this - which is hosted on WSS, and which offers business applications for small businesses. This might be a great opportunity for hosters offering SharePoint to add differentiated lightweight application templates. More on this in a later blog posting.