Ask Learn
Preview
Ask Learn is an AI assistant that can answer questions, clarify concepts, and define terms using trusted Microsoft documentation.
Please sign in to use Ask Learn.
Sign inThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
For decades, you've been able to hold down [Shift] and Right-Click on a folder (or the background of a folder) to get a "Open Command Prompt here" option. ("Copy as path" is also on this menu)
I recently also discovered, that you can open any program using the folder as the current folder by typing a command (e.g. cmd.exe or powershell.exe) in the Address Bar.
In the Windows 10 Creators Update, the default shell is being changed to PowerShell ("Open PowerShell here") -- in light that PowerShell is a more comprehensive shell than CMD.
Looking into how this works, I discovered and realized two things:
The first issue isn't an issue. Adding additional entries is easy -- it just requires additional "shell\<verb>\command" registry entries.
The second observation - the elevation - is the issue. If the target EXE isn't manifested as requiring elevation, you need to use the special verb "runas" to cause the elevation. That's great if you're just adding one entry, but problematic if you want more than one.
What you have to do is to use the "ExtendedSubCommandsKey" concept. This creates a sub-menu. Each sub-menu can have a "runas" key, allowing multiple elevated entries in a context menu tree (one per menu/sub-menu).
The great thing about the "ExtendedSubCommandsKey" concept is that the value is a "reference". Meaning a single configuration can be shared between the folder's node ("Directory\shell\...) and the folder's background ("Directory\background\shell\...) context menu registrations. Both areas point (reference) the "Directory\ContextMenus\shell\..." area -- saving you the need to duplicate the <verb> settings.
Within each sub-menu (each ContextMenu area), you make the ...\shell\<verb>\... keys as normal. The only exception is the menu's name; it is set via a "MUIVerb" REG_SZ, rather than the usual "(Default)" REG_SZ.
In my example below, I have the Command Prompt and PowerShell supported as sub-menus. Within each sub-menu, there is a verb to launch the prompt non-elevated ("open") and elevated ("runas").
What you get is something like this (this example is a right-click of a folder's node):
[caption id="attachment_515" align="alignnone" width="585"]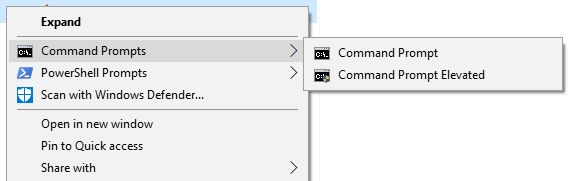 Command Prompt menu[/caption]
Command Prompt menu[/caption]
[caption id="attachment_505" align="alignnone" width="542"]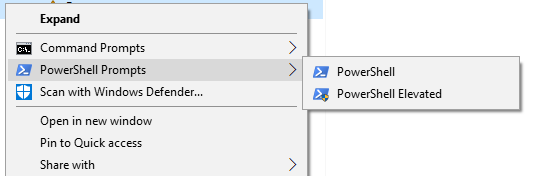 PowerShell menu[/caption]
PowerShell menu[/caption]
You don't have to use it run an application elevated to not. For example, with GIT, it can be use to launch the GIT GUI or GIT BASH.
[caption id="attachment_535" align="alignnone" width="407"]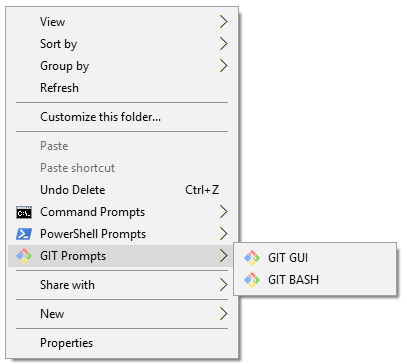 GIT menu[/caption]
GIT menu[/caption]
Icons, UAC and hiding other menus
To make make things look pretty/orderly, I've set the following to add the appropriate icon, indicate UAC, and to hide (unwanted) menus.
ENJOY!
Example: Directory_Prompts.reg
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
; Command Prompt
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\01MenuCmd]
"MUIVerb"="Command Prompts"
"Icon"="cmd.exe"
"ExtendedSubCommandsKey"="Directory\\ContextMenus\\MenuCmd"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\background\shell\01MenuCmd]
"MUIVerb"="Command Prompts"
"Icon"="cmd.exe"
"ExtendedSubCommandsKey"="Directory\\ContextMenus\\MenuCmd"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuCmd\shell\open]
"MUIVerb"="Command Prompt"
"Icon"="cmd.exe"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuCmd\shell\open\command]
@="cmd.exe /s /k pushd \"%V\""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuCmd\shell\runas]
"MUIVerb"="Command Prompt Elevated"
"Icon"="cmd.exe"
"HasLUAShield"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuCmd\shell\runas\command]
@="cmd.exe /s /k pushd \"%V\""
; PowerShell
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\02MenuPowerShell]
"MUIVerb"="PowerShell Prompts"
"Icon"="powershell.exe"
"ExtendedSubCommandsKey"="Directory\\ContextMenus\\MenuPowerShell"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\background\shell\02MenuPowerShell]
"MUIVerb"="PowerShell Prompts"
"Icon"="powershell.exe"
"ExtendedSubCommandsKey"="Directory\\ContextMenus\\MenuPowerShell"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuPowerShell\shell\open]
"MUIVerb"="PowerShell"
"Icon"="powershell.exe"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuPowerShell\shell\open\command]
@="powershell.exe -noexit -command Set-Location '%V'"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuPowerShell\shell\runas]
"MUIVerb"="PowerShell Elevated"
"Icon"="powershell.exe"
"HasLUAShield"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuPowerShell\shell\runas\command]
@="powershell.exe -noexit -command Set-Location '%V'"
; Ensure OS Entries are on the Extended Menu (Shift-Right Click)
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\cmd]
"Extended"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\background\shell\cmd]
"Extended"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\Powershell]
"Extended"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\background\shell\Powershell]
"Extended"=""
Example: Directory_Prompts_GIT.reg
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
; GIT
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\03MenuGit]
"MUIVerb"="GIT Prompts"
"Icon"="C:\\Program Files\\Git\\mingw64\\share\\git\\git-for-windows.ico"
"ExtendedSubCommandsKey"="Directory\\ContextMenus\\MenuGit"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\background\shell\03MenuGit]
"MUIVerb"="GIT Prompts"
"Icon"="C:\\Program Files\\Git\\mingw64\\share\\git\\git-for-windows.ico"
"ExtendedSubCommandsKey"="Directory\\ContextMenus\\MenuGit"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuGit\shell\git_gui]
"MUIVerb"="GIT GUI"
"Icon"="C:\\Program Files\\Git\\mingw64\\share\\git\\git-for-windows.ico"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuGit\shell\git_gui\command]
@="\"C:\\Program Files\\Git\\cmd\\git-gui.exe\" \"--working-dir\" \"%v.\""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuGit\shell\git_shell]
"MUIVerb"="GIT BASH"
"Icon"="C:\\Program Files\\Git\\mingw64\\share\\git\\git-for-windows.ico"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\ContextMenus\MenuGit\shell\git_shell\command]
@="\"C:\\Program Files\\Git\\git-bash.exe\" \"--cd=%v.\""
; Move Official GIT Entries to the Extended Menu (Shift-Right Click)
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\git_gui]
"Extended"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\background\shell\git_gui]
"Extended"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\git_shell]
"Extended"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\background\shell\git_shell]
"Extended"=""
Ask Learn is an AI assistant that can answer questions, clarify concepts, and define terms using trusted Microsoft documentation.
Please sign in to use Ask Learn.
Sign in